LNG to Power – Power Generation projects
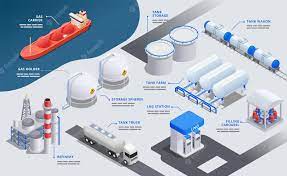
Setup, Process, Equipment, LNG Supply Chain
Liquefied Natural Gas is a transition fuel on the path to clean energy. It is cleaner than other fossil fuels and can help to displace diesel, coal, and other more polluting fuels.
Using LNG and Renewable LNG for small power generation projects is well suited as it can be supplied using ISO containers.
A fast and economical way to provide small-scale LNG is by using ISO Tanks.
The usage of ISO containers for the supply of LNG and Bio-LNG has many benefits such as flexibility, it uses existing transport logistics pathways and infrastructure, it is scalable, safe and quick to implement.
Many companies in Asia and across the world are choosing LNG to replace diesel fuel. However and to achieve low or no CO2 emission, some end users are opting for Fuel cells technology instead of gas generators. Those units can use LNG, Bio-LNG, Biomass or Hydrogen for the fuel. Other technologies exists in the market for companies who want to reduce their CO2 emissions.
Click here to learn more about fuel cells technology for microgrids.
Setup Process for a small power generation project
How to setup a small LNG-to-Power project with supply of LNG using ISO Containers.
- Site Selection: Choose a suitable location for the micro-scale LNG power generation project, considering factors like accessibility, proximity to the load center, and safety considerations.
- Permitting and Regulations: Obtain all the necessary permits and approvals from local authorities and comply with relevant regulations for LNG handling and power generation.
- Infrastructure Development: Develop the necessary infrastructure for the project, including foundation and support for the equipment, LNG unloading and storage facilities, and a power distribution system.
- Equipment Installation: Transport and install the LNG ISO container, vaporizer, gas engine, power generator, and other associated equipment on-site.
- Connection to Load: Establish the electrical connection between the power generator and the load center, ensuring a stable power supply.
- Testing and Commissioning: Thoroughly test all components and systems to ensure they are functioning correctly and safely. Commission the power generation system for regular operation.
- Training and Maintenance: Train the personnel on the operation and maintenance of the equipment. Set up a maintenance schedule to keep the system in optimal condition.
- Continuous Monitoring: Implement remote monitoring and control systems to ensure smooth and efficient operation of the micro-scale LNG power generation project.
It is important to note that the specific requirements for a small or micro-scale LNG power generation project can vary depending on the location, power demand, and local regulations.
Working with experienced engineers, specialists in LNG projects and LNG suppliers capable of delivering LNG in ISO containers will be crucial to ensure a successful LNG project in a remote area or for industrial users.
Equipment (Downstream equipment)
Learn more about the equipment needed for small power generation projects in remote areas (or for industrial users) using LNG by ISO tanks.
- LNG ISO Container (ISO Tanks): This is the primary container that will store and transport liquefied natural gas (LNG) to the remote location. ISO containers are standardized and can be easily transported using trucks, ships, or trains.
- Vaporizer: A vaporizer is essential to convert LNG back into natural gas for combustion. There are different types of vaporizers available, including ambient air vaporizers, water bath vaporizers, and shell-and-tube vaporizers. The choice of vaporizer will depend on factors like the ambient temperature and the required gas flow rate.
- Gas Engine (Gas Generator): The heart of the power generation system will be a gas engine or a gas turbine. Gas engines are more common for micro-scale projects as they are cost-effective and have a high efficiency when operating at a constant load. Gas turbines are more suitable for larger projects with varying power demands.
- Power Generator: The gas engine or gas turbine will be coupled with an electrical generator to produce electricity. The generator should be appropriately sized to meet the power demands of the remote area.
- Control and Monitoring System: A sophisticated control system is essential to regulate the gas supply, manage power generation, and ensure safety. It will also provide remote monitoring capabilities for efficient operation and maintenance.
- Safety Equipment: Safety is a top priority in LNG projects. The installation should include safety measures such as emergency shutdown systems, gas leak detectors, and fire suppression equipment.
- Fuel Storage and Distribution System: Besides the LNG ISO container, there may be a need for additional LNG storage tanks depending on the power demand and the frequency of LNG deliveries. A distribution system will be necessary to route the gas from the storage to the vaporizer and then to the gas engine or turbine.
- Auxiliary Systems: These include systems for fuel heating, fuel conditioning, exhaust gas heat recovery, and waste heat utilization to improve the overall efficiency of the power generation process.
Suggested setup and components for a remote area
Please find below information on how to plan a power generation project for a remote area, an industrial user or other. Setting up a small LNG power generation project requires careful planning and consideration.
- LNG Supply Chain:
• Secure a reliable LNG supplier who can provide regular deliveries of ISO containers to the remote area. Consider contracting with a reputable LNG supplier with experience in remote locations.
• Determine the required LNG consumption rate based on your power generation needs and obtain commitments from the supplier to meet those demands. - LNG Storage and Handling:
• Set up a well-insulated LNG storage facility that can hold multiple ISO containers. The storage capacity should be enough to cover the peak power demands and accommodate potential delivery delays.
• Ensure proper safety measures and procedures are in place for handling and storing LNG. - Regasification Unit:
• Install a reliable regasification unit to convert LNG back to natural gas before it enters the power generation system. Depending on the scale of the project, either a vaporizer or a small-scale liquefaction plant could be used. - Power Generation System:
• Choose a suitable power generation technology that can efficiently utilize natural gas. Gas turbines or gas engines are common choices for small-scale LNG power projects.
• Size the power generation system appropriately to meet the anticipated load demands, with some extra capacity to handle unforeseen spikes in demand. - Backup Power and Energy Storage:
• Consider incorporating backup power sources, such as diesel generators or battery energy storage systems, to ensure continuous power supply during LNG delivery interruptions or maintenance periods. - Monitoring and Automation:
• Implement a comprehensive monitoring and automation system to keep track of LNG inventory, power generation, and equipment performance.
• Integrate remote monitoring capabilities to enable real-time supervision and swift response to any issues. - Logistics and Transportation:
• Plan the logistics of LNG transportation from the storage facility to the power generation site, ensuring efficient and timely delivery.
• Create contingency plans for extreme weather conditions or other factors that may impact transportation. - Safety and Regulatory Compliance:
• Adhere to all safety regulations and best practices for handling LNG, especially in remote areas where emergency response might take longer.
• Comply with local, national, and international regulations related to LNG storage, handling, and power generation. - Environmental Considerations:
• Assess the environmental impact of the project and implement measures to mitigate any potential negative effects on the surrounding ecosystem. - Maintenance and Support:
• Establish a regular maintenance schedule for all equipment and infrastructure to ensure reliable and efficient operation.
• Have a team of skilled technicians trained to handle any maintenance issues that may arise.
Remember, the success of a small-scale LNG power generation project in a remote area depends on careful planning, reliable suppliers, efficient equipment, and proper maintenance. Always consult with experts and relevant authorities to ensure a safe and compliant setup.
Click here to learn more about all aspects of large LNG-to-Power projects. Get access to articles & webinars covering the mitigation of Risk, Finance and Construction, infrastructure, FSRU, Case study in Asia, etc.
LNG supply chain using ISO containers
LNG Supply Chain using ISO tanks for small LNG to Power project.
Wether the LNG containers are delivered to the destination port (CFR/CIF basis) or directly at the end user’s site, it is important for customers to ensure a reliable, stable and constant supply of LNG.
Click here to learn more about the LNG & Bio-LNG virtual pipeline.
The small-scale LNG supply chain involves the following elements:
A. LNG Production and Liquefaction:
• Identify and engage with LNG suppliers who produce and liquefy natural gas. Ensure they have the capacity to meet the project’s monthly LNG volume requirement.
B. LNG Transportation:
• Arrange for the transportation of LNG from the production facility to a storage terminal or distribution point near the remote area.
• Use ISO containers or cryogenic tankers to transport LNG to the storage terminal.
C. Storage Facility:
• Set up an intermediate storage facility near the remote area to store and regasify the LNG before delivery to the micro LNG power generation site.
D. Local Transport:
• Organize local transportation of LNG from the storage terminal to the micro LNG power generation site.
• Utilize specialized vehicles capable of handling cryogenic LNG.
E. LNG Unloading and Storage:
• Install equipment at the micro LNG plant to safely unload LNG from the transport vehicles.
• Store the LNG in cryogenic storage tanks or ISO containers at the power generation site.
Contact us if you are looking for a turnkey LNG supply solution, LNG procurement, Equipment, or if you need help regarding your LNG-to-Power project.
